Masculinity extends beyond mere male sexual potency, with the XY chromosome pair determining biological sex during fetal development. The Y chromosome dictates male sex, while the X chromosome establishes female sex. Furthermore, the Y chromosome contributes to androgen production, which are sex hormones responsible for male physical attributes such as genitalia dimensions and configuration, sperm production, hair growth patterns, bone structure, and vocal cord and voice box development.
These masculine characteristics influence a man’s appearance and self-confidence, prompting many to seek ways to enhance their masculinity. Such enhancements may include cultivating thicker eyebrows, body or facial hair, increasing muscle mass, and improving sexual performance.
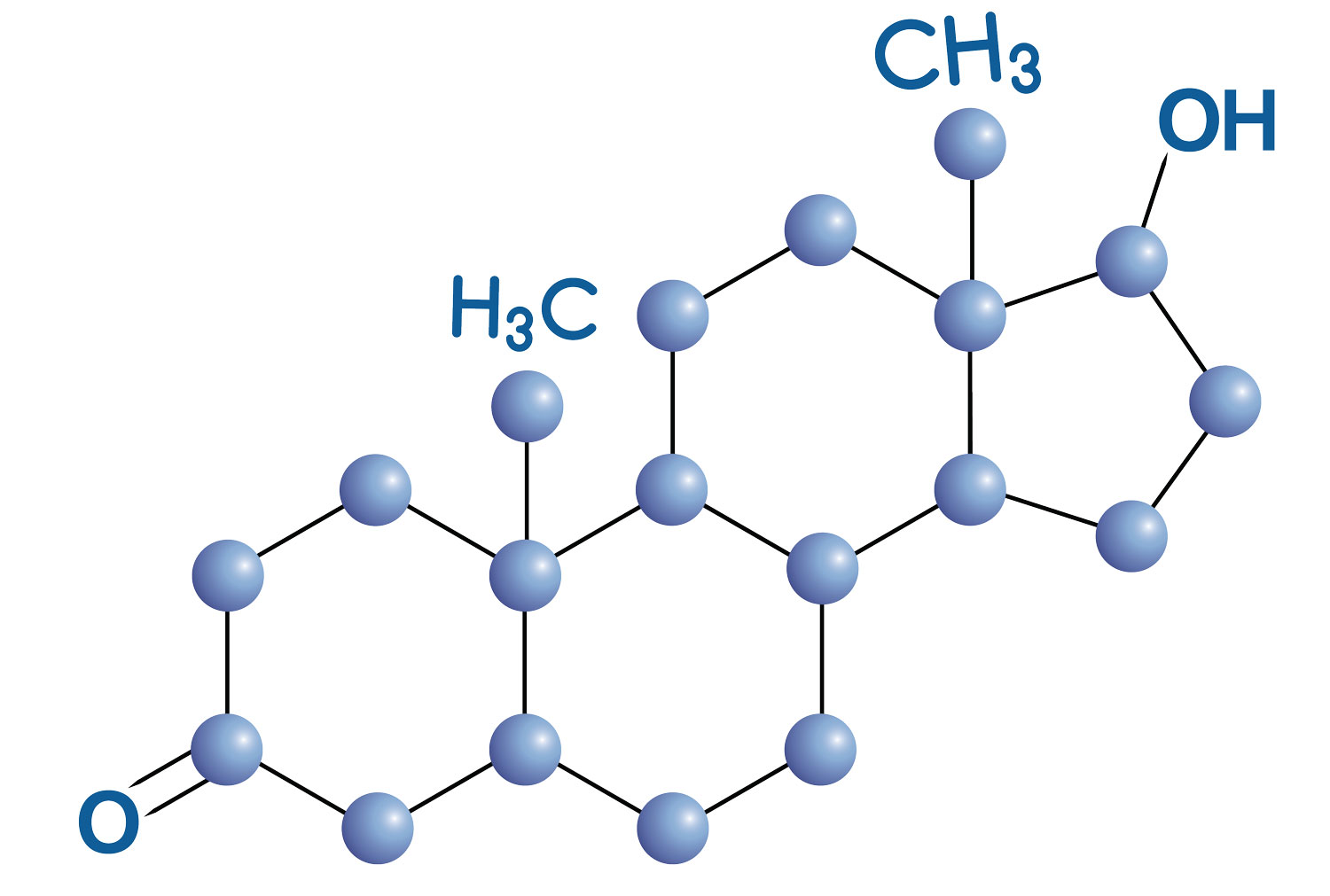
Testosterone constitutes the majority of androgens. Andropause, a condition involving hormonal fluctuations, can lead to stress, mood swings, irritability, lack of focus, insomnia, chronic fatigue, reduced physical energy, diminished sexual potency, decreased muscle mass, increased abdominal fat, and hair thinning
The Durascience™ Research Institute in the United States has been investigating the scientific principles contributing to men’s stamina improvement. The principle, termed M.B.M™ (Men Balance Matrixes), emphasizes the components essential for optimizing men’s vitality.

Genetics play a crucial role in androgen production and metabolism within the body, helping maintain testosterone balance. Disruptions in this process can cause abnormal androgen fluctuations, affecting various systems within the male body. Androgen receptors (AR) are found in male body cells, binding to androgens like testosterone or dihydrotestosterone and initiating various intracellular activities. The AR gene, located on the X chromosome at Xq 11-12, controls the androgen receptor. If this gene becomes dysfunctional, it can disrupt androgen production and function, leading to Androgen insensitivity syndrome (AIS). AIS may impact penis development and cause abnormal neuron functions in males, such as Kennedy’s disease, which manifests as muscle weakness, enlarged breasts, testicular atrophy, sterility, diabetes, and other symptoms.
Numerous scientific studies confirm the significant influence of the gut microbiome on the digestive system, immune system stimulation through GALT (Gut-Associated Lymphatic Tissue), and nutrient absorption. Research also indicates that the gut microbiome affects androgen balance. Factors like high-carbohydrate foods can disturb the balance of the gut microbiome.
Maintaining appropriate and adequate nutrition is key to preserving androgen balance. Nutritional imbalances can lead to androgen dominance or deficiency, with negative consequences on the body, ranging from mild to severe. Androgen imbalances can also affect mental health, causing mood swings and depression. Insufficient nutrition, both in quality and quantity, can contribute to unbalanced testosterone levels. However, restoring androgen balance is possible by focusing on the nutritional content of each meal.
Cells in the body encounter free radicals such as ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species) and RNS (Reactive Nitrogen Species), produced by normal metabolic processes and external sources. When free radicals accumulate excessively, oxidative stress occurs, damaging proteins, fats, and DNA within cells and causing cell degeneration. Cellular dysfunction can lead to various diseases, including androgen production imbalances and male reproductive system regression. A robust antioxidant system directly affects cell function concerning hormone production and balance. Research has shown that adequate antioxidant intake in male subjects positively impacts testosterone levels and the production of sufficient, high-quality sperm.

Androgen hormones play a crucial role in human physical development, regulating male genital growth, muscle development, vocal depth, and other masculine attributes. During childhood and pre-adolescent years, androgen hormone levels remain low, with a strong genetic predisposition being essential for adequate production. Puberty triggers physical development, accentuating male characteristics.
In adult males, androgen hormones circulate in the bloodstream, binding to target cell receptors to ensure optimal cellular function. This process relies on the critical protein Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin (SHBG), with genetics accounting for approximately 50% of SHBG efficiency. Genes implicated in SHBG formation control include PRMT6, GCKR, ZBTB10, JMJD1C, SLCO1B1, NR2F2, ZNF652, TDGF3, LHCGR, BAIAP2L1, and UGT2B15, among others.
Andropause is characterized by a decline in testosterone levels, resulting in physical changes. Testosterone, a hormone responsible for stimulating masculine characteristics, influencing the male reproductive system, and impacting various bodily functions such as muscle building, fat burning, bone strength, voice tone, and libido, begins to decrease after the age of 30. This decline leads to alterations in physical and mental health, with andropause correlating with a roughly 1% annual decrease in sexual desire.
Breast milk is fundamental for infants, providing nourishment and supporting gut microbiota development. A balanced gut microbiota ensures healthy hormonal balance during puberty.
As individuals age, gut microbiota influences metabolic processes and male sex hormone production. Imbalances in gut microbiome, whether due to beneficial or harmful bacteria, can disrupt the digestive system. Bacteria produce detrimental endotoxins, such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS), which damage the intestines and rapidly diffuse into the bloodstream, leading to chronic inflammation and testosterone deficiency (TD).
Providing children with a healthy, nutritious diet ensures their bodies receive essential nutrients to regulate the endocrine system. During puberty, a balanced endocrine system effectively produces and disseminates growth hormones. Moreover, the endocrine system regulates the production of other hormones, including androgen, to maintain equilibrium.
Adults also require proper nutrients to nourish and regulate the endocrine system, testes, and adrenal glands for efficient sex hormone and androgen production.
Men experiencing andropause still need adequate essential nutrients for their endocrine systems, even if their reproductive systems exhibit signs of regression.
In conclusion, appropriate nutrition is vital for males of all ages to maintain hormonal balance.
From birth to puberty, human bodies are continuously exposed to various free radicals, resulting in cellular and tissue damage. During childhood, cells are still new and efficient in producing antioxidant substances to combat harmful free radicals, ensuring normal bodily functions and hormone production at different ages.
Every day, trillions of body cells are exposed to free radicals, either ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species) or RNS (Reactive Nitrogen Species), produced by cellular metabolism. When free radicals accumulate, a condition called “oxidative stress” occurs, disrupting proteins, fats, and DNA throughout the body. This leads to cell degeneration, malfunction, and various diseases, including estrogen disorders and male reproductive system regression.
Thus, it is imperative to bolster the antioxidant system in adult males and men with andropause to ensure efficient cell function and hormone production for hormonal balance.
The Consequences of M.B.M™ Component Deficiency
Inheritance of atypical traits from parents or grandparents may lead to hormonal imbalances, particularly concerning sex hormones produced by the endocrine system. While such anomalies may appear minor, they can culminate in significant health complications, such as Disorders of Sexual Development (DSD), manifesting as gender disorders between childhood and adolescence.
Inherited genetic disorders persistently affect the endocrine system, analogous to a compromised foundation undermining a structure. As men approach andropause, these inherited traits may become more conspicuous, giving rise to symptoms such as erectile dysfunction, diminished metabolism, osteoporosis, muscle loss, hot flashes, hair loss, insomnia, mood swings, lack of motivation, and memory loss.
Childhood represents a critical phase in human development, during which bacterial imbalances can induce chronic inflammation and compromise organ function. For instance, imbalances can affect the brain, liver, and endocrine system, responsible for producing various hormones. Disrupted androgen balance can adversely impact bone development, resulting in short stature.
In adulthood, the human body harbors both beneficial and harmful bacteria. Ideally, these bacteria collaborate to maintain equilibrium. However, imbalances can impair the digestive system, causing chronic inflammation and perturbed organ function, particularly in the brain and endocrine system. As men transition into andropause, addressing bacterial imbalances becomes crucial, as they can profoundly affect their bodies and expedite the manifestation of abnormalities.

Ensuring optimal nutrient intake for the body’s needs is vital at all life stages. However, inadequate or excessive nutrient consumption can influence sex hormone production within endocrine glands. Excessive sex hormone production can hinder bone development and sexual characteristics, while other organs, such as the pancreas, may become dysfunctional. In males, insufficient sex hormone levels can affect bone mass and brain cell activity.
Chronic inflammation within the body can impact endocrine glands, culminating in the malfunction of sex hormone production. Maintaining appropriate hormone production is essential for preserving overall health and well-being, and disruptions can have far-reaching consequences on an individual’s health.

Practical Solutions for Holistic Health and Wellness
Presently, a multitude of studies are exploring the associations between gene disorders and androgen function, enhancing our comprehension of the risks associated with diverse diseases. Nevertheless, additional research is imperative before these discoveries can be incorporated into practical medical interventions.

Achieving a balanced gut microbiome can be facilitated through the consumption of prebiotics, which are non-digestible polysaccharides that aid in optimizing gut bacterial balance and fostering a favorable intestinal environment for these bacteria to proliferate. Conversely, probiotics are live, beneficial bacteria that contribute to a healthy digestive system and gut microbiome.
Ensuring children receive age-appropriate, comprehensive nutrition from childhood through puberty is crucial, as nutrition directly influences the production of essential hormones for physical development, particularly during puberty when the body undergoes fluctuations in sex hormones.

1. Calciferol: Present in marine fish, eggs, and milk, calciferol functions as a hormone in the body. Protein deficiency can result in decreased sex hormone levels, while calcium boron elevates male sex hormone levels.

2. Zinc: Abundant in meat, eggs, soybeans, cereals, and oysters, zinc is vital for numerous bodily functions and is renowned for enhancing male sex hormones. Zinc deficiency correlates with androgen decline, which can be addressed with zinc supplementation.

3. Phenol: Phenol stimulates the antioxidant system and promotes testosterone, the male sex hormone responsible for physical masculinity. Furthermore, phenol improves male fertility by increasing sperm count and quality.
Given the prevalence of environmental pollution, UV radiation, and irritant chemicals from personal care products, it is essential to bolster the immune system to combat free radical-induced cellular damage. This damage can lead to chronic inflammation, cellular and chromosomal damage, cell degeneration, and hormonal dysfunction.
Antioxidants function akin to a battery, supplying negative ions to free radicals and transporting the ROS/RNS system catalyst away from the cell, thereby mitigating oxidative stress chain reactions.
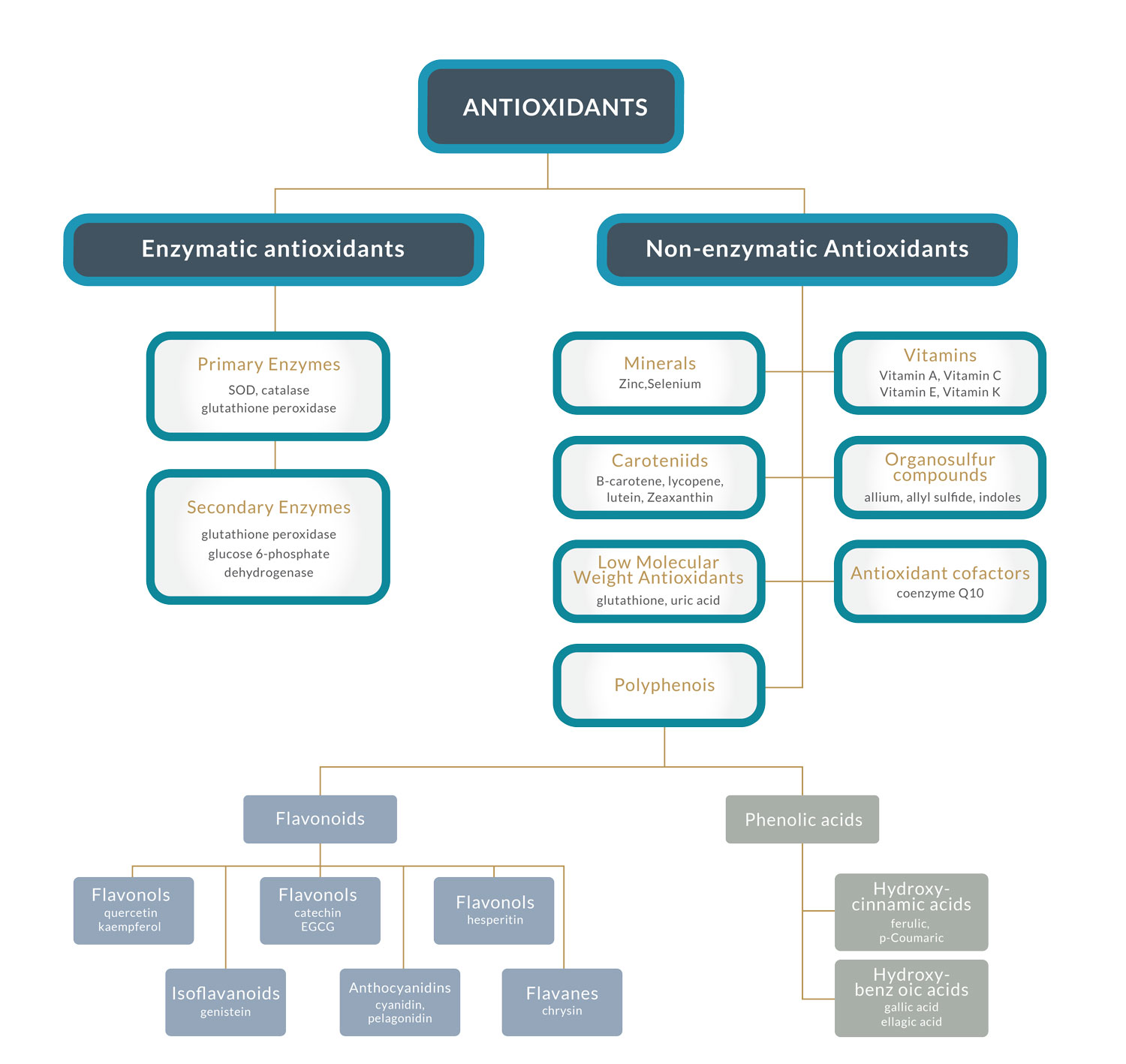
Antioxidants can be categorized into two groups: enzymatic antioxidants and non-enzymatic antioxidants.
- Enzymatic Antioxidants execute enzyme-related functions, such as Superoxide Dismutases (SODs), Catalase, and the Glutathione System.
- Non-enzymatic Antioxidants encompass Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C), Glutathione, Melatonin, Tocopherols and Tocotrienols (Vitamin E), Carotenoids, Flavonoids, and Uric Acid.




Consistent consumption of antioxidant-rich foods aids in reducing the quantity of detrimental free radicals capable of disrupting the body’s systems and cellular DNA.
As individuals age, their bodies weaken, and the endocrine system may malfunction due to genetic or other factors. Additionally, an imbalanced gut microbiome and reduced sex hormone production, coupled with daily exposure to free radicals, contribute to the decline of masculine traits at varying ages.
In light of these considerations, Durascience™ has formulated M.B.M™ – Men Balance Matrix, a product designed to augment masculinity and bolster confidence, empowering men to take pride in healthy relationships founded on effective sexual potency.
